The idea behind making machines think like humans might seem like a sinister plot for a science-fiction film or novel. Pop culture has tagged AI with varying perceptions of people. Some believe that artificial intelligence can support humans in achieving new heights of technological advancements. On the contrary, discussions about artificial intelligence explained for beginners also draw attention to examples from the Terminator film franchise.
The Terminator films show that an AI named Skynet has taken control of the world and enslaved humans. No one would like to endanger their future by achieving a faster route to digital advancements. However, the ideal course of action for utilizing AI to its full potential would focus on learning about AI and its benefits.
Level up your AI skills and embark on a journey to build a successful career in AI with our Certified AI Professional (CAIP)™ program.
Where Did the Concept of AI Find its Roots?
One of the first things you would need to learn about AI is the outline of its history. Evidence and examples about thinking machines have been traced back to ancient Greece. On the other hand, some of the notable milestones in the evolution of AI provide a better perspective on the roots of artificial intelligence.
Alan Turing introduced the possibilities for association between computing machinery and intelligence in 1950 with a research paper. The next important milestone in the history of artificial intelligence points to the coining of the term in 1956. John McCarthy came up with the name artificial intelligence, and the same year also marked the development of the first AI software program.
The outline of AI examples in the pages of history starts with neural networks. Frank Rosenblatt created a neural network-based computer in 1967. The computer was capable of learning through trial and error and led to promising advancements in the field of neural networks. Subsequently, new developments in neural networks and the creation of deep neural networks fuelled the growth of the AI ecosystem from 1997. Most recently, the industry has been characterized by the exponential growth of large language models, such as ChatGPT.
Definition of Artificial Intelligence
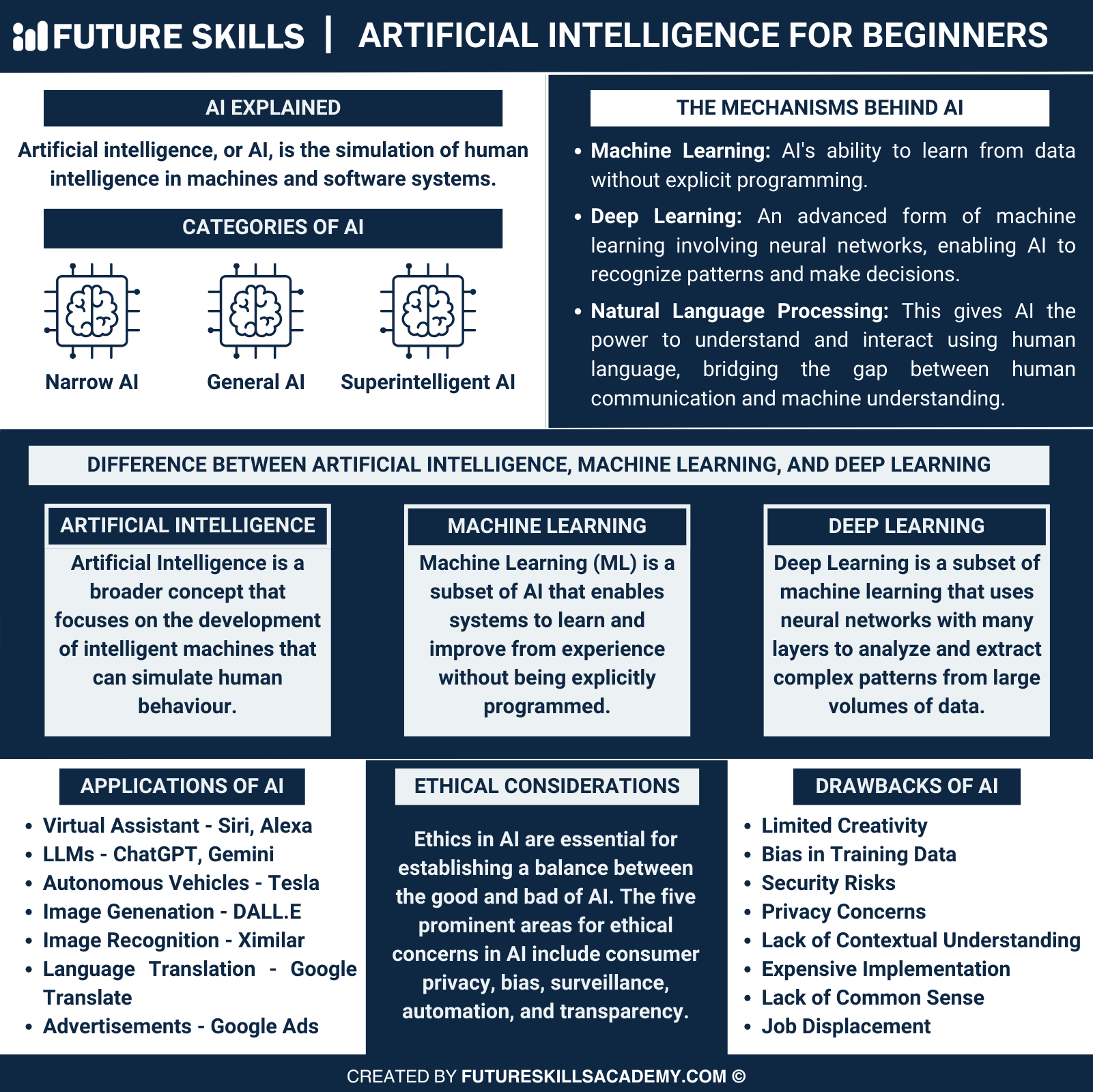
The history of AI provides a glimpse of its potential, which has expanded consistently over time. Beginners are more likely to think about answers to “What is AI?” in their search for information about artificial intelligence. Interestingly, you can find multiple explanations for defining artificial intelligence, which can lead to confusion. The first-ever definition of AI suggests that it is the science and engineering involved in the creation of intelligent machines or intelligent computer programs.
Artificial intelligence is a field of computer science that relies on strong datasets to offer problem-solving benefits. It also includes subdomains, such as deep learning and machine learning, which are used synonymously with artificial intelligence. Machine learning and deep learning algorithms help in creating intelligent systems capable of using input data to make suitable classifications and predictions.
Level up your ChatGPT skills and kickstart your journey towards superhuman capabilities with Free ChatGPT and AI Fundamental Course.
Working of Artificial Intelligence
The next prominent highlight you must explore in a guide to artificial intelligence is the working mechanism of AI. Continuously accelerating hype for artificial intelligence has encouraged vendors to promote how they adopt AI. How does AI work in real-world use cases? Most of the use cases of artificial intelligence involve the use of an important component of AI, such as machine learning.
Artificial intelligence works through a combination of specialized software and hardware for developing and training machine learning algorithms. The AI definition provides clarity regarding the fact that artificial intelligence does not depend on a single programming language. On the other hand, C++, Python, R, Julia, and Java are some of the top languages preferred for AI development.
The working of artificial intelligence or AI systems focuses on the ingestion of massive amounts of labeled training data. In the next step, AI systems would conduct data analysis to derive correlations and patterns. You should also utilize the newly identified patterns for making predictions regarding future states of transactions.
One of the most common AI examples of chatbots can show you how they can take examples of text and learn to generate interactions that appear real. Similarly, an image recognition tool can use AI to learn how to identify and describe images from different examples. Beginners should also note that AI programming emphasizes cognitive skills such as the following,
-
Learning
Learning is a vital highlight of AI programming, which relies on data collection and establishing rules for turning data into actionable insights. It is one of the crucial artificial intelligence features for creating algorithms that transform computers into intelligent machines.
-
Reasoning
Artificial intelligence or AI also focuses on reasoning, which is important for the selection of the right algorithm to achieve desired outcomes.
-
Creativity
AI uses the creativity aspect with neural networks, statistical methods, and rule-based systems. The primary goal of creativity in AI systems revolves around utilizing AI techniques for generating new images, text, audio files, ideas, and videos.
-
Self-correction
The working of artificial intelligence explained for beginners also sheds light on the continuous fine-tuning of algorithms. Self-correction aspect in AI programming emphasizes the necessity of achieving accuracy in results.
Want to gain practical skills in using OpenAI API and implementing API calls to facilitate LLM interactions, Enroll now in the Certified Prompt Engineering Expert (CPEE)™ Certification.
How Many Types of AI Can You Find Today?
The two most popular categories of artificial intelligence are narrow or weak AI and general or strong AI. You can also find another specialized category of artificial intelligence in the form of super AI. Let us dive deeper into the distinct traits you can find with different artificial intelligence variants.
-
Narrow AI
Narrow artificial intelligence or weak AI is one of the notable variants of AI, which is important for voice assistants. It offers you a broader answer to “What is AI?” by showcasing powerful functionalities in examples like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa. Narrow AI focuses on intelligent systems created to address specific tasks and solve distinct issues without any explicit design variation. It is also known as weak AI due to the lack of general intelligence.
Apart from voice assistants, you can also find examples of weak AI tools for flagging inappropriate content, image-recognition systems, and technologies for responding to simple customer support requests. One of the most popular examples of narrow AI or weak AI is ChatGPT, which has been programmed for a specific task.
-
General AI
General artificial intelligence or strong AI is a hypothetical concept for describing programming that could replicate the cognitive abilities associated with the human brain. The general AI examples would show you that strong AI can deal with unfamiliar tasks by employing fuzzy logic. General AI systems support knowledge transfer from one domain to the other, alongside ensuring autonomous discovery of solutions. Strong AI can feature the same reasoning power as a human.
It is important to note that general artificial intelligence focuses on understanding intellectual tasks and abstract thinking. General artificial intelligence would also involve learning from experiences and using the inferred knowledge to solve new problems. As of now, the goal of creating a completely conscious AI system is considerably far in the future.
-
Super AI
While the concept of a strong AI seems to be far from reality, the definition of super AI can create more interest in artificial intelligence. As a matter of fact, super AI is one of the first things you think about before you learn AI fundamentals. Super AI refers to artificial intelligence systems which ensure that the intelligence of machines outperforms all types of human intelligence. The possibilities of super AI turning into reality are still under research, and such a system can exist only in hypothetical settings.
Excited to understand the crucial requirements for developing responsible AI and the implications of privacy and security in AI, Enroll now in the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Course
Variants of Artificial Intelligence Use Cases
The applications of AI can be divided into four different categories based on the underlying philosophy. You can categorize artificial intelligence systems based on applications and working principles into the following types.
-
Reactive Machines
Reactive machines are one of the most popular additions to an AI definition guide for understanding the potential of AI. The primary work of reactive machines is to respond to specific tasks according to pre-programmed instructions. It is also important to note that reactive machines do not have any memory. One of the most popular examples of reactive machines is Deep Blue, the AI chess program by IBM. It can work by identifying different pieces of a chessboard for making relevant predictions.
-
Limited Memory
Limited memory AI systems feature memory for using past experiences to decide the course of actions in the future. The development of limited artificial intelligence features relies on consistent training of models for analysis and utilization of new data. During the use of limited memory AI in machine learning, programmers must follow crucial steps such as establishing training data and creating a machine learning model. Subsequently, you must ensure that the model can make relevant predictions and receive feedback. Limited memory AI systems must also store feedback in the form of data alongside enabling reiteration of all the steps.
-
Theory of Mind
Theory of Mind AI systems is one of the most appealing yet hypothetical variants of artificial intelligence. You can explore a guide to artificial intelligence explained for beginners to find how the Theory of Mind AI revolves around creating machines that can understand emotions.
It revolves around the principle that other entities also have emotions and thoughts which would influence their behavior. In the case of AI, the Theory of Mind points out that AI could understand the emotions and feelings of humans, animals as well as other machines. As a result, it could make decisions and predict behavior in ways that would empower future use cases in human teams.
-
Self-Awareness
Self-awareness AI systems are also other prominent additions among AI examples for the future. Self-awareness AI systems are similar to super AI, with the power of self-consciousness. Machines with self-awareness could understand their existing state and other environmental factors to predict their future state. As of now, the concept of self-awareness AI is still in the pipeline.
Enroll now in the AI for Business Course to understand the role and benefits of AI in business and the integration of AI in business.
Notable Examples of Artificial Intelligence Technology
The interest and hype around artificial intelligence technologies have created a sudden spike in searches for examples of artificial intelligence. Interestingly, artificial intelligence has become an integral part of the existing society in different ways. For example, Google Maps and IBM Watson are prominent examples of widespread AI usage for general users and businesses. Here are some of the most noticeable AI technologies which have gained a lot of attention.
-
Automation
The foremost example of powering technology with AI is the use of Robotic Process Automation or RPA. Robotic Process Automation is a type of software that helps in automation of rules-based and repetitive data processing tasks. In combination with machine learning, AI could deliver more advanced functionalities.
-
Machine Learning
Machine learning is one of the most popular aspects in answers to “What is AI?” as a subdomain of AI. The examples of different types of machine learning models can showcase how artificial intelligence transforms the tech landscape. For instance, supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning serve distinct models for creating intelligent machines.
-
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing, or NLP, is another significant example of AI technology that can revolutionize the world. The existing use cases of natural language processing revolve around speech recognition, text translation, and sentiment analysis.
-
Machine Vision
Machine Vision or computer vision is crucial for capturing and analyzing visual information through a camera, digital signal processing, and signal conversion. Some of the most common applications of such AI use cases point to the applications for medical image analysis and signature identification.
Become a certified ChatGPT expert and learn how to utilize the potential of ChatGPT that will open new career paths for you. Enroll in Certified ChatGPT Professional (CCGP)™ Certification.
Conclusion
The most common references to artificial intelligence, explained in popular literature, revolve around the future of AI. As a matter of fact, most people are concerned about artificial intelligence features becoming powerful enough to replace their jobs. AI can take away your jobs if you don’t learn how to use it for your benefit in the long run.
Therefore, it is important to dive deeper into artificial intelligence fundamentals and its important subdomains. Explore other details, such as the differences between AI, machine learning, and deep learning, alongside reflecting on popular AI use cases.